Are you a beginner in micro controller projects?and are you stuck where to start from?if yes,then this is one of the simplest mini projects that you can start from . This mini project will give you a clear understanding of programming your micro controller. we sometimes look at our watch and wonder " how does this thing work". Well, in this digital clock project, you will gain some insight on how micro controller can be used to make it work as a Digital Clock.
Components required:
- 1 microcontroller 89C52(89S52 will also do)
- 2 ceramic capacitors-22pF
- 1 switch(button for reset purpose)
- 1 electrolytic capacitor-10uF,25V
- 1 crystal oscillator-11.0592MHz
- 16x2 LCD display
- 1 resistor-10k
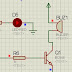
Circuit diagram
Software you will need
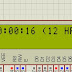
This project has been done in proteus software.If you are new to proteus software, the tutorials given below may get you started with the software.note:if you are familiar with proteus you can skip this part.The programming of the microcontroller is done using keil compiler.port 2 of 89C52 is used as the output port.whereas port 1 is used as the input port.when P1_4 is grounded the 12 hr mode is activated and when P1_5 is grounded the 24 hr mode is activated.In the schematic diagram P1_5 is grounded so the 24hr mode is activated.it is as shown below
Code:
The detail explanation of the code is done below:
#include "REGX52.H"
#include "delay.h"
#include "lcd.h"
void main(void)
{
int hr=0; /*initiate hour=0 */
int min=0; /*initiate minutes=0 */
int sec=0; /*initiate seconds=0 */
P1=0xff; /*set port 1 as input port */
P2=0x00; /*set port 2 as output port*/
while(1)
{ LCD_INIT(); /*initialize LCD*/
if (P1_4==0)/*if P1_4 is grounded enter the 12hr loop */
{
for (sec=0;sec<60;sec )
{
LCD_DisplayNum(hr,2);
LCD_STRING(":");
LCD_DisplayNum(min,2);
LCD_STRING(":");
LCD_DisplayNum(sec,2);
LCD_STRING(" (12 HR)");
delay_sec(1);
LCD_CLEAR();
if (sec==59)
{
min=min 1;
if(min==60)
{
if(hr==11&&min==60&&sec==59)
{hr=0;min=0;sec=0;}
else
{ hr=hr 1;
min=0;}
}
}
} }
else
{
if(P1_5==0) /*if P1_5 is grounded enter the 24hr loop */
{
for (sec=0;sec<60;sec )
{
LCD_DisplayNum(hr,2);
LCD_STRING(":");
LCD_DisplayNum(min,2);
LCD_STRING(":");
LCD_DisplayNum(sec,2);
LCD_STRING(" (24 HR)");
delay_sec(1);
LCD_CLEAR();
if (sec==59)
{
min=min 1;
if(min==60)
{
if(hr==23&&min==60&&sec==59)
{hr=0;min=0;sec=0;}
else
{ hr=hr 1;
min=0;}
}
}
} }}
LCD_INIT();
}
}
you can download the .hex file here
schematic diagram
main.c
digclk.hex
you can add more functions to this digital clock since 2 ports of 89C52 are still unused.For instance, you can connect a buzzer to port 4 such that the buzzer sounds at a specified time or you can connect a keypad to port 0 such you can set the timings externally.
Please comment if you would further like to improve the project.